Linux File Systems for Windows does support the Linix Logical Volume Manager (LVM) partitions. This allows a disk partition to contain multiple logical partitions. LVM differs from an extended. Formerly known as Paragon ExtFS, Linux File Systems for Windows is an application designed specifically for all those users who need to access data on their Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 partitions from their.
Linux Reader™ is a popular and free software product, and it remains non-commercial freeware. Since version 4.0, there are extra features that are available as Linux Reader Pro™.
With Linux Reader Pro™, you can read files from even more file systems, get remote access through an SSH connection, create a virtual drive, export files via FTP, and more.
All significant features of Linux Reader™ remain free: no annoying advertising, no trial mode, no restrictions.
Important to Know
Both Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™ provide you with safe, read-only access to the source drive. Moreover, Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™ bypass file security policies, so you can access any file on a Linux disk.
System requirements for Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™: Windows 7, 8 or 10.
Linux Reader™ Specifications
Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™ provide you with access to files on the following file systems:
- Ext2/3/4
- ReiserFS, Reiser4
- HFS, HFS+(reader)
- FAT, exFAT
- NTFS, ReFS
- UFS2
- RomFS(reader)
- RAID 0, 1, 4, 5, 50, 10, and JBOD
- APFS (reader mode)
- ZFS (preview only*)
- XFS (preview only*)
- Hikvision NAS and DVR (preview only*)
* Linux Reader Pro™ license is required to obtain full access to files.
Linux Reader Pro™ Specifications
In addition to the file systems mentioned above, Linux Reader Pro™ provides full access to these additional file systems:
- ZFS
- Encrypted APFS
- XFS
- Hikvision NAS and DVR
- Encrypted BitLocker disks
With Linux Reader Pro™, you can also remotely access files via SSH on Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, QNX, Mac OS, and other Unix-like file systems.
The brilliant features of Linux Reader Pro™ allow you to:
- Map any disk or files onto a new drive letter.
- Export files to an FTP server.
Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™ Essentials
Both Linux Reader™ and Linux Reader Pro™ have the following features:
- Read files from all types of hard drives, including SSD, HDD, flash drives, memory cards, and others.
- Read-only access to files in Linux drives, leaving the original files intact.
- Free preview of the contents of files to ensure integrity.
- Access any files on Linux system, bypassing security policies.
- Create a disk image of the drives you have access to. In the event of data loss, you can restore the whole drive from this image. This is the most popular feature and the easiest way to restore a drive, according to Linux Reader™ users.
For the moment, DiskInternals Linux Reader™ is the premier software tool on the market, providing you with access from Windows to various Linux file systems like Ext2/Ext3/Ext4, HFS, ReiserFS, and others.
You are welcome to download the free version of Linux Reader™ right now. This version allows you to upgrade to Linux Reader Pro™.
How to Read Linux Files on Windows
Step-by-step instructions:
- 1. First, you need to download and install Linux Reader™.
- 2. Then, run Linux Reader™ and choose the drive you want to open.
- 3. Linux Reader™ shows you all the available files, including pictures, videos, documents, and other files. Select any file to preview its content by right-clicking the mouse and choosing ”Preview in New Window”. Preview is absolutely free and does not oblige you to pay anything.
- 4. You can save files from Linux to Windows:
- 5. To access files remotely via SSH protocol, to export files from file systems supported by Linux Reader Pro™ only, to map files as a virtual drive, or to export files to the FTP server, you will need a Linux Reader Pro™ license, which you can easily purchase online. The license also gives you free updates of Linux Reader Pro™ software for 12 months and priority in technical support.
Please, download the completely free version of Linux Reader™ with the option of upgrading to Linux Reader Pro™.
FREE DOWNLOADVer 4.8, WinUpgrade to PROFrom $29.95
- Linux Reader
- Features
- Linux Reader Guide in Pictures
- Screenshots
- About a bash date command
- How to Access Linux Ext2 or Ext3 on Windows
- How to Access Ext4 from Windows
- How to Mount Ext4 on Windows for Free
- Mount Linux Drive on Windows for Free
- Bash Script: All You Need to Know
- An Algorithm: How to Create Bash While Loop
- Linux Shell: What You Need to Know at First
- 5 Basic Shell Script Examples for Your First Script
- How to Use Shell Script Sleep Command
- Bash: How to Check if the File Does Not Exist
- Bash Time Command on Linux
- How to use bash get script directory in Linux
- How to Check Bash String Equality
- How to Use Linux Wait Command
- Bash: How to Loop Through Files in Directory
- 20 Examples of Bash Find Command
- Bash Cat Command in Examples
- Bash Script SSH: How to Use It
- Bash: A Script For User Input
- Linux ZSH: the basic you need to know
- Basic of Grep in Linux Shell Script
- Shell Script Cut: Basic You Need to Know
- Bash: How to Check if String Not Empty in Linux
- Bash: how to split strings in Linux
- Linux: Sudo in Bash Scripts
- Hello World Script in Bash
- A Linux bin/bash Shell
- Linux: New Line in Shell Script
- Linux: Bash String Ends With
- Linux: Bash Printf Examples
- Linux: Bash First Line
- Linux: $0 in a Shell Script
- Linux: A Bash Startup Script
- Linux: Write a Shell Script
- Shell Script: Replace String in File
- A crontab service shell script
- A Bash Multiline Command
- Bash and sh: is there any difference
- A Bash Dirname Command
- Linux: A Bash Source Command
- A Bash to Loop through Lines in File
- Linux: A Bash Linter
- A Bash Nested Loop
- A Bash Test Command
- Use a Shell Script to Send an Email
- A Bash Status of Last Command
- Linux: A Bash Basename Command
- Using Bash to Write to a File
- About Bash Language
- Bash for Loop in One Line
- AWK in a Bash Script
- Learn about useful bash scripts
- Learn about systemd startup script
- About chaining bash commands
- Learn about a bash error code
- Using a bash tee command
- About a bash export command
- Learn about a bash wait command
- Arch Linux install script
- About advanced bash scripting
- To run a shell script in Dockerfile
- About a bash UNTIL loop
- Learn about C shell script
- Learn about Korn shell scripting
- Using /usr/bin/env command
- Whether bash waits for command to finish
- Using bash if 0
- Using && in an IF statement in bash
- If you want to run shell script in background
- The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer error
- Learn about SFTP in bash scripting
- Learn to run Perl script in Linux
- Examples of using the Expect
- Copy command in shell scripts
- Shell script usage
- Install Oracle Database
- Here is everything you need to know about Bash for Windows
- Ext2/3/4
- ReiserFS, Reiser4
- HFS, HFS+
- FAT, exFAT
- NTFS, ReFS
- UFS2
- ZFS (preview only*)
- XFS (preview only*)
- Hikvision NAS and DVR (preview only*)
EFS Recovery - repair your EFS files from damaged or formatted disks
RAID Array Data Recovery - make your RAID arrays alive
VMFS tools - repair your data from VMFS, VMDK, ESX(i), vSphere disks
VMFS Recovery™RAID Recovery™Partition RecoveryUneraser™NTFS RecoveryEFS Recovery™DVR Recovery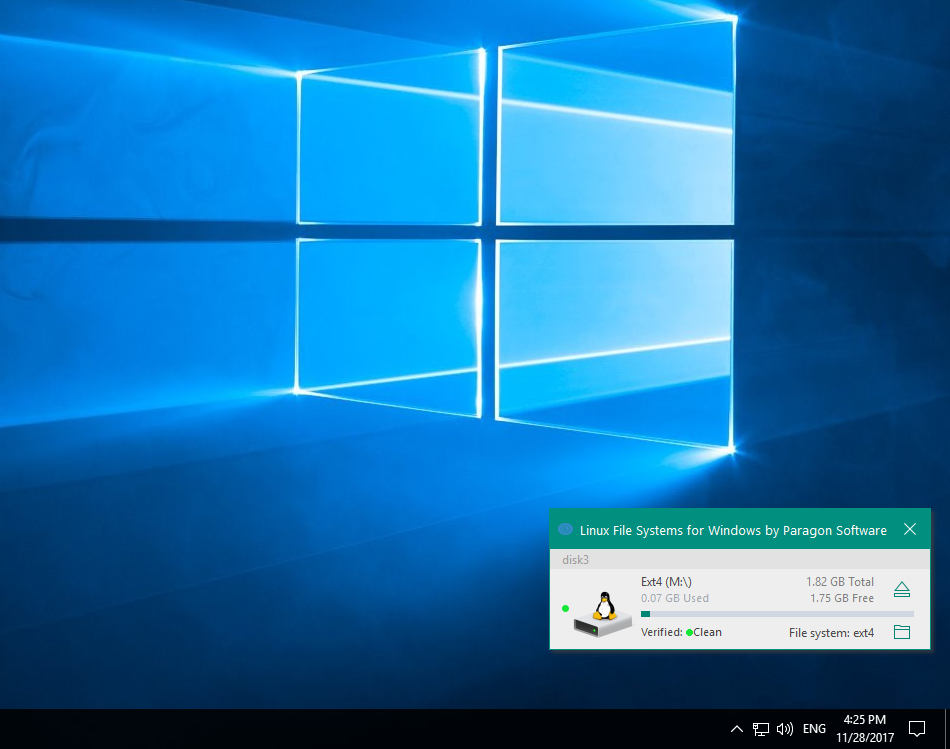
Windows 10 now allows you to mount physical disks formatted using the Linux ext4 filesystem in the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2.
Linux filesystems, such as ext4, cannot be natively accessed in Windows 10 without installing special drivers.
Starting with Windows 10 preview build 20211, WSL 2 now includes a wsl --mount command that lets you mount ext4 and other Linux kernel supported filesystems, directly in installed WSL distributions.
Linux File System For Windows By Paragon
This feature is especially useful for users who dual-boot Windows 10 and Linux and would like to access their Linux drives while using Windows.
How to mount a disk in WSL 2
Once Windows 10 preview build 20211 is installed, you can use the wsl --mount command to mount a disk in WSL 2.
To mount a drive, you should first open a PowerShell command prompt with Administrative privileges and run the following command to get a list of available drives.
Read Ext4 Windows 10
If a disk has a single partition, you can mount it using the command:
Otherwise, if you wish to mount a particular partition, you would use the commands:
Finally, to unmount a disk from WSL 2, you would use the following commands:
By default, wsl --mount will attempt to mount the partition using ext4. To specify a different filesystem, you can use the following command:
When mounted, the disk will be accessible in a Linux distribution under /wsl/[mountpoint].
More detailed instructions on how to use the wsl --mount command can be found here.
To illustrate how these commands work, you can see the image below from Microsoft.
To access a mounted filesystem in Windows 10's File Explorer, you can open the Linux category and navigate to /mnt.
It should be noted that when you mount a disk in WSL 2, it will be available for all WSL 2 Linux distributions that you have installed.
Furthermore, when mounting a partition, the whole disk is mounted and thus will become inaccessible to other applications that may normally use it.
'Also please note that this feature comes with the limitation that only physical disks can be attached to WSL 2. At this time, it’s not possible to attach a single partition,' Microsoft notes.
Related Articles:
